Set Up Ansible Development Desktop
Categories:
Projects:
c2platform/phx/ansible , Ansible Linux Role ( c2platform.core.linux)
, Ansible Win Role ( c2platform.wincore.win)
Overview
Using the PHX
development environment, this guide walks you through
creating a node named pxd-ubuntu-devtop. This node simulates an
Ansible development desktop used in the PHX domain and data center. It is
based on Ubuntu 24.04 with Ubuntu Desktop and XRDP installed for remote access.
Visual Studio Code is also pre-installed. The setup joins the node to an Active
Directory (AD) domain, similar to desktops in the PHX domain.
After following these steps, the node will be ready for domain user Tony to perform Ansible engineering tasks.
Prerequisites
- Setting Up the PHX Development Environment on Ubuntu 24.04
- The node
pxd-admust be running, aspxd-ubuntu-devtopwill join the AD domainC2.ORGmanaged by this node.
Setup
To provision the development node pxd-ubuntu-devtop, run the following
command. This process takes about 13 minutes.
vagrant up pxd-ubuntu-devtop
Verify
Domain Membership
The pxd-ubuntu-devtop node automatically joins the Active Directory (AD)
domain managed by Ansible. To confirm it is part of the c2.org domain, run the
following command:
realm list
vagrant@pxd-ubuntu-devtop:~$ realm list
c2.org
type: kerberos
realm-name: C2.ORG
domain-name: c2.org
configured: kerberos-member
server-software: active-directory
client-software: sssd
required-package: sssd-tools
required-package: sssd
required-package: libnss-sss
required-package: libpam-sss
required-package: adcli
required-package: samba-common-bin
login-formats: %U
login-policy: allow-realm-logins
Login as Tony and Become Root
Verify that you can log in as the domain user tony (password:
Supersecret!
.
Run the following command:
ssh tony@pxd-ubuntu-devtop
Show me
User tony has permissions to become root:
sudo su -
Run exit to become user Tony again:
exit
Passwordless Login Using Kerberos to Linux and Windows Hosts
Kerberos is a network authentication protocol that enables secure, ticket-based
authentication across systems, allowing passwordless access once a user has
obtained a Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT). In this setup, after logging in as
tony on pxd-ubuntu-devtop, you receive a Kerberos TGT. This enables seamless
SSH logins to other domain-joined hosts without re-entering credentials,
provided the hosts are configured for Kerberos authentication.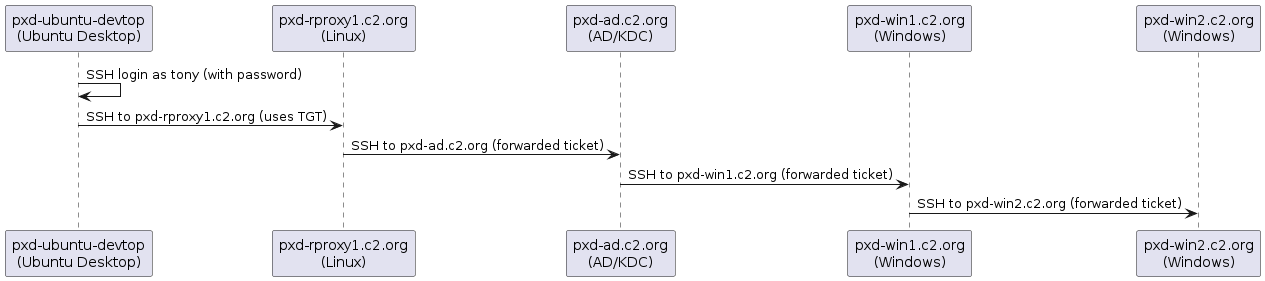
You can view the TGT by running:
klist
tony@pxd-ubuntu-devtop:~$ klist
Ticket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_496801104_TWhKJq
Default principal: tony@C2.ORG
Valid starting Expires Service principal
11/28/25 05:04:48 11/28/25 15:04:48 krbtgt/C2.ORG@C2.ORG
renew until 11/29/25 05:04:48
11/28/25 05:05:03 11/28/25 15:04:48 host/pxd-rproxy1.c2.org@C2.ORG
renew until 11/29/25 05:04:48
This allows Tony to log in to the reverse proxy node pxd-rproxy1 without a
password prompt:
ssh pxd-rproxy1.c2.org
From pxd-rproxy1, user Tony can SSH into the AD controller pxd-ad.c2.org:
ssh pxd-ad.c2.org
This will show a shell similar to below:
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Install the latest PowerShell for new features and improvements! https://aka.ms/PSWindows
PS C:\Users\tony>
On pxd-ad, you now also have a TGT, which you can see using klist:
klist
PS C:\Users\tony> klist
Current LogonId is 0:0x137acc4
Cached Tickets: (1)
#0> Client: tony @ C2.ORG
Server: host/pxd-win1.c2.org @ C2.ORG
KerbTicket Encryption Type: AES-256-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96
Ticket Flags 0x60a10000 -> forwardable forwarded renewable pre_authent name_canonicalize
Start Time: 11/28/2025 5:11:40 (local)
End Time: 11/28/2025 15:04:48 (local)
Renew Time: 0
Session Key Type: AES-256-CTS-HMAC-SHA1-96
Cache Flags: 0x8 -> ASC
Kdc Called:
PS C:\Users\tony>
This allows Tony to SSH further into another Windows node pxd-win1 without a
password prompt:
ssh pxd-win1.c2.org
Because the pxd-win1 host is configured to be trusted for delegation, we can
SSH hop further without a password prompt to pxd-win2.
ssh pxd-win2.c2.org
This trust is also configured by Ansible, see Configure Trust for Delegation in Active Directory for more information.
Review
Vagrant
The Vagrant box pxd-ubuntu-devtop is based on the C2 Platform box
ubuntu24-lxd. This configuration creates a Vagrant box pxd-ubuntu-devtop
based on
LXD and running Ubuntu 24.04 LTS. The setup includes labels that
define
Ansible groups for targeted automation and configuration.
100 - name: ubuntu-devtop
101 description: Ansible Development Desktop
102 box: ubuntu24-lxd
103 ip-address: 192.168.60.11
104 plays:
105 - dev/desktop
106 labels:
107 - desktop
108 - ubuntu_devtop
109 - radix_guardian
28 name: c2platform/ubuntu22-desktop
29 version: 0.1.0
30 provider: lxd
31 labels: [ubuntu, lxd, ubuntu22]
32 ubuntu24-lxd:
Note
Through the dynamic inventory plugin for Vagrant, the assigned labels translate into Ansible groups, which target the host and provide configuration via group variables. Thus, the hostpxd-ubuntu-devtop
belongs to the Ansible groups ubuntu, lxd, ubuntu24, desktop,
ubuntu_devtop, and radix_guardian.Ansible Play
The Ansible play that targets the hosts in the ubuntu_devtop group uses two
roles:
---
- name: Ubuntu Ansible Development Desktop
hosts: ubuntu_devtop
become: true
roles:
- { role: c2platform.core.linux }
- { role: c2platform.wincore.win }
The inclusion of the Windows role may seem unusual at first, but it addresses a
key requirement for Kerberos functionality. Proper Kerberos operation relies on
accurate reverse DNS lookups on Ubuntu hosts. To support this, the setup creates
DNS pointer records (PTR records) for each Ubuntu host on the AD controller
pxd-ad using the Ansible module win_dns_record. The Windows role handles
this based on the configuration shown below. Note that this configuration
applies to the Ansible group ubuntu, meaning the policy of creating PTR
records extends to all Ubuntu hosts.
---
win_roles: []
win_resources:
- name: "{{ '.'.join(ansible_eth1.ipv4.address.split('.')[-2::-1]) }}.in-addr.arpa"
module: win_dns_zone
type: Primary
replication: Domain
state: present
delegate_to: pxd-ad
- name: "{{ ansible_eth1.ipv4.address.split('.')[-1] }}"
module: win_dns_record
type: "PTR"
zone: "{{ '.'.join(ansible_eth1.ipv4.address.split('.')[-2::-1]) }}.in-addr.arpa"
value: "{{ inventory_hostname }}.{{ px_ad_domain_name }}"
state: present
delegate_to: pxd-ad
Ansible Configuration
To better understand how
Ansible provisions the
Ansible development desktop pxd-ubuntu-devtop, examine the relevant
group variables. These are stored in the following folders:
group_vars/all: policy for all hosts, including Linux and Windows.group_vars/ubuntu: policy for Ubuntu hosts.group_vars/ubuntu_devtop: policy for Ubuntu-based Ansible development desktops.
Policy for Ansible Development Desktops
The folder
group_vars/ubuntu_devtop
contains two files: group_vars/ubuntu_devtop/main.yml and group_vars/ubuntu_devtop/kerberos.yml.
group_vars/ubuntu_devtop/main.yml
---
linux_resources:
devtop:
- name:
- virtualenv
- ubuntu-desktop
- xrdp
- snapd
- gedit
- libsecret-tools
- seahorse # GNOME Keyring GUI
type: package
- name: code
type: snap
classic: true
- name: firefox
type: snap
- name: Vault client scripts
type: copy
defaults:
mode: "0755"
resources:
- dest: /usr/local/bin/vault-client.sh
src: vault-client.sh
- dest: /usr/local/bin/vault-client-keyring.sh
src: vault-client-keyring.sh
- name: Create disable screen lock script
type: copy
dest: /usr/local/bin/disable-screen-lock.sh
mode: "0755"
content: |
#!/bin/bash
gsettings set org.gnome.desktop.screensaver lock-enabled false
gsettings set org.gnome.desktop.session idle-delay 0
rm -- "$0"
- name: Create autostart desktop file
type: copy
dest: /etc/xdg/autostart/disable-screen-lock.desktop
content: |
[Desktop Entry]
Type=Application
Exec=/usr/local/bin/disable-screen-lock.sh
Hidden=false
NoDisplay=false
X-GNOME-Autostart-enabled=true
Name=Disable Screen Lock
Comment=Disable screen lock on startup
group_vars/ubuntu_devtop/kerberos.yml
---
linux_resources:
devtop-kerberos:
- name:
- python3-dev
- krb5-user
- libkrb5-dev
type: package
Next Step
With pxd-ubuntu-devtop created and configured, proceed to the next step:
setting up the
Ansible development environment on this desktop in a way
that simulates the configuration in the air-gapped PHX domain.
Additional Information
- Ansible Inventory Project: A structured collection of files used for managing hosts and configurations. It typically includes inventory files, playbooks, host configurations, group variables, and Ansible vault files.
- Use Dynamic Inventory in Development: Guideline for using dynamic inventory in Ansible development environments as a concrete example to illustrate future full automation for organizations new to Ansible.
- Configure Trust for Delegation in Active Directory: Example of managing trust for delegation in Active Directory for Windows hosts using the win_resources variable in the Windows role.
- How to set up SSSD with Active Directory - Ubuntu Server documentation
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.